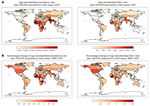
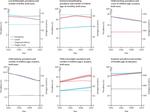
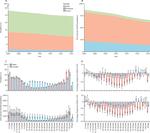
Everyone, all over the world, deserves to live a long life in full health. In order to achieve this goal, we need a comprehensive picture of what disables and kills people across countries, time, age, and sex. The Global Burden of Disease (GBD) provides a tool to quantify health loss from hundreds of diseases, injuries, and risk factors, so that health systems can be improved and disparities can be eliminated.
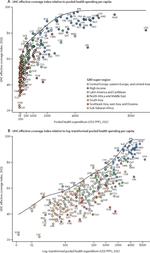
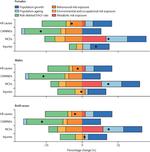
To align health systems with the populations they serve, policymakers first need to understand the true nature of their country’s health challenges – and how those challenges are shifting over time. GBD research incorporates both the prevalence of a given disease or risk factor and the relative harm it causes, in addition to just estimating disease prevalence.
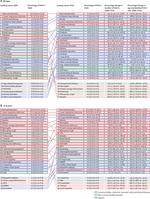
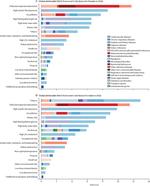
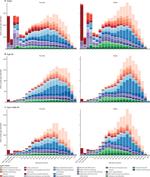
The tools allow decision-makers to compare the effects of different diseases, such as malaria versus cancer, and then use that information at home. IHME has created a suite of interactive data visualizations that allow people to make sense of the over 1 billion data points generated.
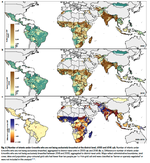
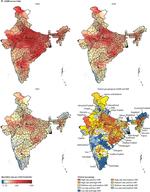
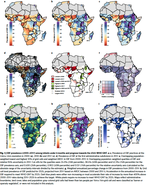
The Global Burden of Disease is collected and analyzed by a consortium of more than 9,000 researchers in 162 countries and territories. The data capture premature death and disability from 370 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, by age and sex, from 1990 to the present. The GBD’s flexible design allows it to be used at the global, national, and local levels to understand health trends over time.
Will Gardner
Research Scientist
My research interests include global maternal and child health, respiratory epidemiology, and health metrics and statistical modeling.